A Comparative study of anxiety disorders treatment with Paroxetine in combination with cranial electrotherapy stimulation therapy.
LU Ling, HU Jun. A Comparative study of anxiety disorders treatment with Paroxetine in combination with cranial electrotherapy stimulation therapy. Medical Innovation of China, 11(08):080-082, 2014.
Device
Alpha-Stim®
Key Variable
Anxiety
Objective
The objective was to explore the add-on effect of cranial electrotherapy stimulation therapy in the treatment of anxiety disorders.
Design
Randomized controlled trial, (N=120)
Primary Effectiveness Endpoint
Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAM-A)
Secondary Outcome Measures
Clinical Global Impression Scale (CGI-SI)
WHO Quality of Life questionnaire (WHOQOL-BREF)
Protocol Summary
Patients enrolled in the study (N=120) entered the 6 week treatment phase after a one-week washout period. The control group was given 10 – 20 mg of paroxetine (Paxil) daily while the treatment group received the same daily dose of paroxetine (10 – 20 mg) in combination with daily cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) treatments. The treatment course was 6 weeks in duration. The primary measurement of efficacy was reductive ratio in the HAM-A and CGI-SI with ≥75% being clinically cured, 50 – 74% obviously improved, 25 – 49% improved and <25% as ineffective. The WHO quality of life measurement was used to measure quality of life factors at baseline and week 6.
Device Application Protocol
Subjects were treated with Alpha-Stim CES at 0.5 Hz, between 50 – 500 μA for 60 minutes daily for a total of 42 days. In the first treatment investigators increased the current until the subjects reported a tingling or dizziness. At that point the current was reduced to a subsensory level. The subjects were then treated at this level for the duration of the study.
Data Analysis
A database was created and SPSS 15.0 software was used for statistical analysis of the data obtained. The measurement data was expressed as ( ), t-tests were used for comparison. The enumeration data was tested with χ2, where P
Results
Subjects
The control group (N=60) received 10 – 20 mg of paroxetine while the treatment group (N=60) received 10 – 20 mg of paroxetine combined with daily CES treatments.
Baseline Measurements: Group Equivalence
There was no statistical difference between the control and treatment groups at baseline.
HAM-A
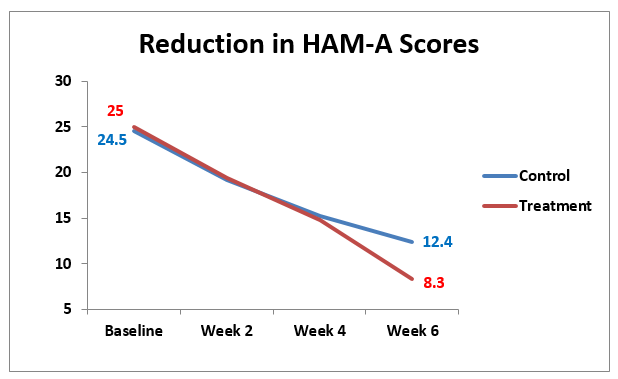
Both the control and the treatment groups showed improvement in HAM-A scores with each consecutive measurement. The comparison of HAM-A scores showed no significant changes between control and treatment groups at baseline, week 2 or week 4 but there was a significant difference in the two groups at week six (p<0.01). The treatment group which consisted of daily paroxetine and CES improved significantly more than the control group which received paroxetine alone.
Figure 1. This graph compares the improvement in anxiety scores between the CES treatment and control groups which was significant (p<0.05) at 6 weeks.
CGI-SI
The control group and the treatment group yielded significant improvement from baseline to the six week endpoint. While both groups reported significant improvement, there was more improvement in the treatment group and the difference between the control and treatment groups was also statistically significant (p<0.05).
WHOQOL-BREF
The quality of life scores reduced significantly (p<0.05) over the 6 week treatment course in both groups but of the 4 domains there was only a significant difference between the control and treatment groups in the physical domain (p<.05).
Conclusion
The results of this study showed that six weeks of combining paroxetine with daily CES treatments, yielded significant improvement over paroxetine alone on the HAM-A scale from baseline to 6 weeks out. This was confirmed with the HAM-A (p<0.01) and the CGI-SI (p<0.05). There was also a significant reduction in quality of life however there was no significant difference between the control and treatment groups except in the physical domain (p<0.05).